REASONING IN VECTOR SPACE: AN EXPLORATORY STUDY OF QUESTION ANSWERING
是ICLR2016的一个论文,主要讲的是bAbI上面用一套vector推导的方法来搞
Our exploration sheds light on designing more sophisticated dataset and moving one step toward integrating transparent and interpretable formalism of TPR into existing learning paradigms
就是现在的这个理论还是不很成熟,用一套非常简单的的规则系统就可以搞好了
In this paper, we endeavor to disentangle the problem cleanly into semantic parsing, knowledge encoding, and logical reasoning.
===============================
作者首先将问题分为
3.1 CONTAINEE-CONTAINER RELATIONSHIP
也就是包含,和包含者的关系,如下面的三个
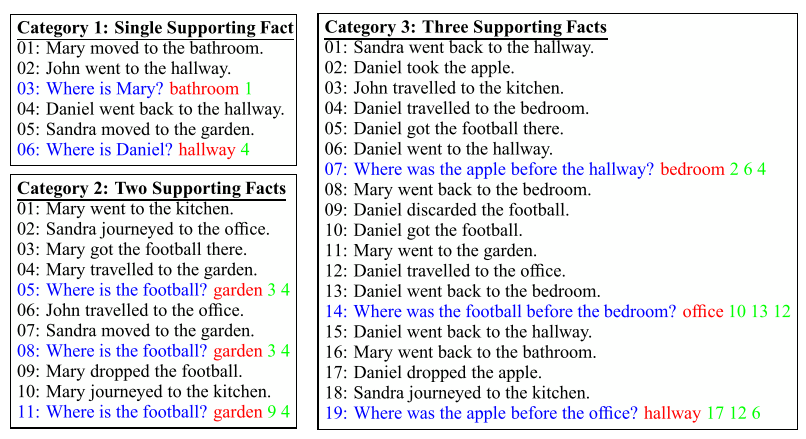
对于上面的第一类或者第二类问题,首先作者将各种的实体(人,物,地点)表示成一个向量,然后当“包含”这个关系出现的时候:比如:小明走进了教室,这里小明
就是containee,而教室就是container。我们就用外积 in tensor notation, (containee) ⊗ (container), or in matrix notation, (containee)(container) T— and then stored in a slot in a memory,来表示这个规则
比如有下面的这个东西
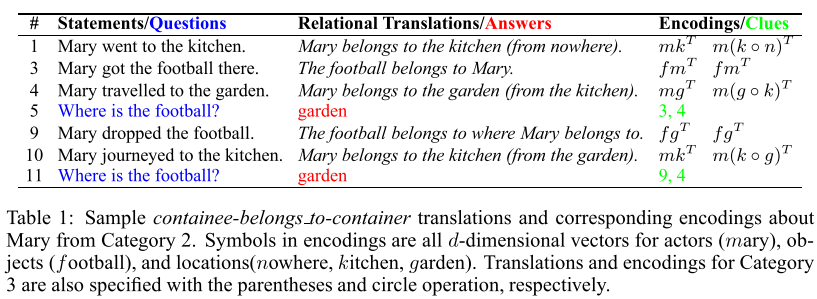
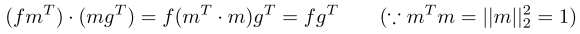
其中fmg都是实体的向量缩写
而右边的那个clues是指的 x把y给z的这种关系,可以在
◦: Rd × Rd −→ Rd. This binding operation maps a pair of (next, prev) location vectors into a d-dimensional vector via a d × 2d temporal encoding matrix U like the following
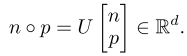
就是把一个东西以前和现在的从属关系给弄到一个空间里面
3.2 MULTIPLE RELATIONSHIPS
在这种问题里面,有很多种关系,不仅仅是包含和被包含的关系了,这个时候关系有很多种
Path Finding |||Positional Reasoning 是其中的两个
对于东南西北这种关系,我们可以这样的来处理
We assume given four d × d non-singular matrices N, E, W, S encoding four different directions satisfying N = S −1and E = W −1
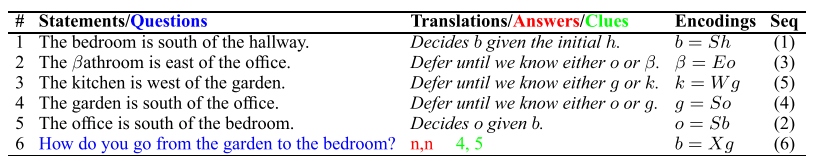
这就是其中的一个,关系之间也有关系,所以可以用这种方法最后推导出来。
------------------
还有好多,所以可以都用这种方法来搞定
作者比较的东西在下面这个里面体现(下面是以前的实验的结果)
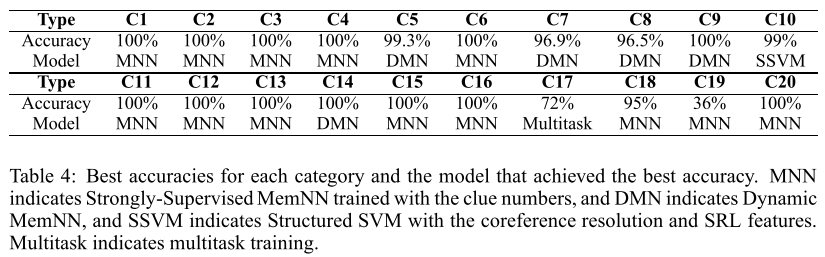
而作者用这种矩阵操作的方法得到的结果如下所示
所有的都是非监督的 真心牛逼啊
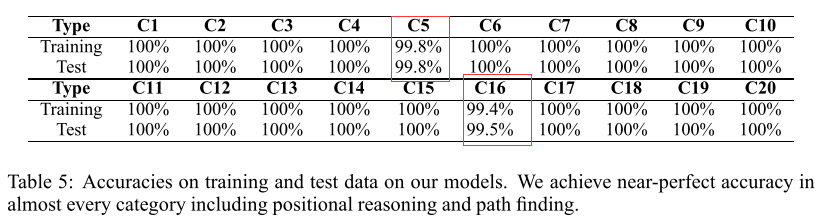
回复列表: